The Theory of Business

The theory of Business is a human artifact that is not very long-lived. Great American companies of the 1920s were based on theories that did not work, while the IBM and Deutsche Bank of Japan failed on their own theories. In today’s world, the keiretsu theory and the universal bank theory are both failing to produce the desired results. A business theory must change as the environment changes. Otherwise, it could never be effective.
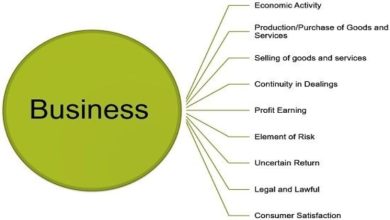
There are several types of business enterprises. Some are small, single-person operations while others are large companies across many industries. A successful business would be Apple or Walmart. Companies are defined by their industry, which relates to what they sell. For example, a company may be in the real estate business, an advertising business, or a mattress-producing business. Depending on the nature of the business, the term “business” may include both a for-profit and a non-profit enterprise.
Businesses have different goals and objectives. While traditional business concept involves generating profits by selling a product or service, modern businesses aim to satisfy their customers. Business processes can be optimized to maximize profit while providing enough revenues to cover expenses and pay the owners. To accomplish these objectives, businesses use employees, which perform certain functions for them. They need to stay updated on industry trends to remain competitive. They should always keep looking for new tools and equipment to make their businesses more efficient.